
Substances or materials that undergo in combustion are known as fuels of combustion. The high ratio of surface-to-volume increases loss of heat. Micro combustion is combustions whose combustion processes take place in very small volumes.

Example, phosphorous ignites on itself at room temperature without heat application.Ĭombustion that results in a turbulent flame is mostly utilized for industrial applications as the turbulence helps in fuels and oxidizer mixing process.
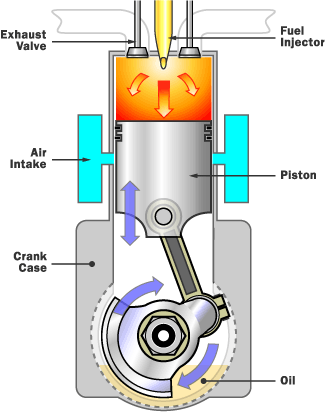
It is a type of combustion that occurs through self-healing, pursued by thermal runaway and then, finally ignition. This combustion is intermittently known as explosion combustion. This reaction is used in the form of machinery like internal combustion engines and thermobaric weapons. Rapid combustion otherwise known as fire is a type of reaction which releases a large amount of heat and light and results in a flame often. Solid materials that undergo smoldering combustion includes materials like coal, cellulose, cotton, tobacco, wood, foams etc. Typically, it is an incomplete form of the combustion reaction. This form of combustion is slow, flameless and a low-temperature combustion, undergone by the heat evolved when the surface of the fuel is directly attacked by oxygen. In this type of combustion, products which are pyrolysis remains unburnt and contaminate the resulted smoke with noxious gases. This combustion is the same as complete combustion, it also produces water, but instead of carbon dioxide, the product is carbon and carbon monoxide.
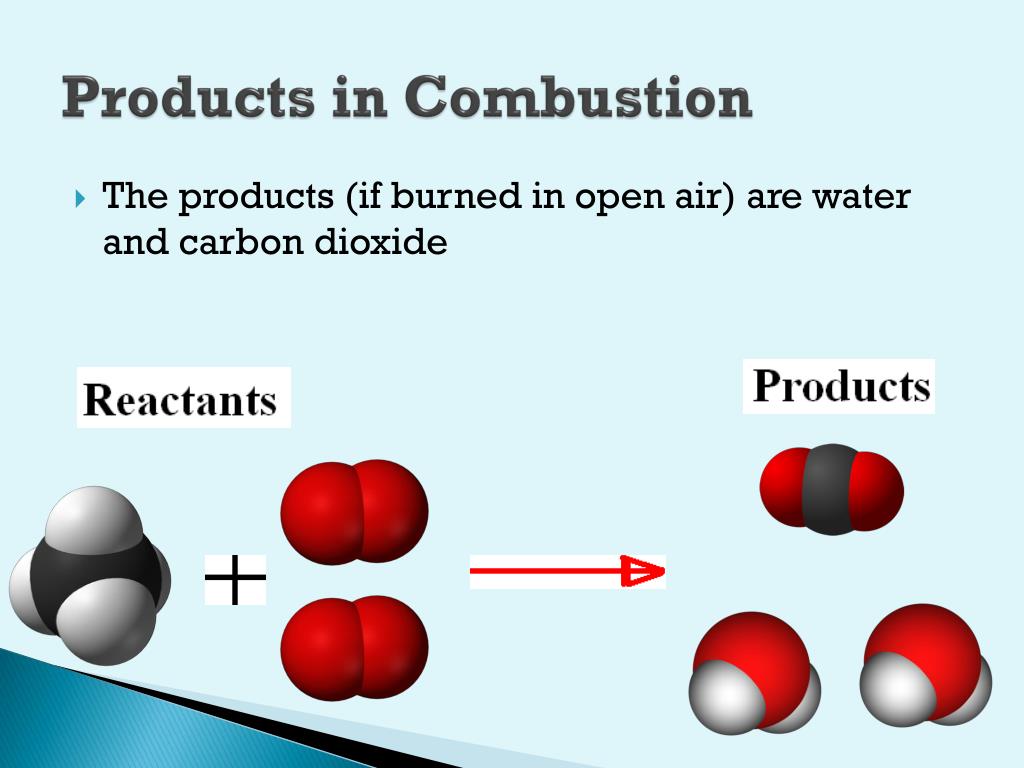
This combustion takes place when there doesn’t exist enough oxygen, allowing fuel to react completely producing carbon dioxide and water. Carbon produces carbon dioxide, sulfur yields sulfur dioxide, and iron returns iron (III) oxide.
When different elements are burned, the products of those are primarily common chemical oxides. When a hydrocarbon is burnt in oxygen, the reaction yields carbon dioxide and water primarily. Types of Combustion: Complete and Incomplete Combustion:ĭuring complete combustion, the reactant burns in oxygen and produces products that are limited. Combustion reaction or burning is an exothermic redox chemical reaction at a high temperature between a reductant or fuel and an oxidant that produces oxidized, usually gaseous products in the form of heat and light.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
